前言: 了解 ES 的索引管理方法有助于扬长避短,更好的利用 ES 的强大功能,特别是当遇到性能问题时,原因通常都可回溯至数据的索引方式以及集群中的分片数量。如果未能在一开始做出最佳选择,随着数据量越来越大,便有可能会引发性能问题。集群中的数据越多,要纠正这一问题就越难,本文旨在帮助大家了解 ES 容量管理的方法,在一开始就管理好索引的容量,避免给后面留坑。
为什么要做容量管理
- 在生产环境使用 ES 要面对的第一个问题通常是索引容量的规划,不合理的分片数,副本数和分片大小会对索引的性能产生直接的影响。
- Elasticsearch 中的每个索引都由一个或多个分片组成的,每个分片都是一个 Lucene 索引实例,您可以将其视作一个独立的搜索引擎,它能够对 Elasticsearch 集群中的数据子集进行索引并处理相关查询。
- 查询和写入的性能与索引的大小是正相关的,所以要保证高性能,一定要限制索引的大小,具体来说是限制分片数量和单个分片的大小。
- 分片和索引的大小太大和太多容易导致性能问题。
官方博客建议的分片数量
注意: ES 官方推荐分片的大小是 20G - 40G,最大不能超过 50G。
如何管理 ES 的容量
在介绍了为何要管理ES的容量后,我们接下来需要考虑的是如何进行管理,以下为通常的做法。
1. 使用在索引名称上带上时间的方法管理索引
例如: <logs-now{yyyyMMddHH+08:00}-000001>
需要注意的是,在使用 HTTP 接口创建索引时,索引名称要进行 urlencode 编码:
1.1 写入和查询索引
# 创建索引
$ PUT /%3Cnginxlogs-%7Bnow%7ByyyyMMddHH%7C%2B08%3A00%7D%7D-000001%3E
{
"aliases": {
"nginxlogs-read-alias": {}
}
}
# 返回结果
{
"acknowledged" : true,
"shards_acknowledged" : true,
"index" : "nginxlogs-2020061518-000001"
}
# 写入数据
$ POST /%3Cnginxlogs-%7Bnow%7ByyyyMMddHH%7C%2B08%3A00%7D%7D-000001%3E/_doc
{"name":"xxx"}
{
"_index" : "nginxlogs-2020061518-000001",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "VNZut3IBgpLCCHbxDzDB",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 2,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 0,
"_primary_term" : 1
}
# 查询数据
## 使用多索引查询
$ GET /nginxlogs-2020061518-000001,nginxlogs-2020061519-000001/_search
{"query":{"match_all":{}}}
## 使用通配符查询多索引
$ GET /nginxlogs-*/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "nginxlogs-2020061518-000001",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "VNZut3IBgpLCCHbxDzDB",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "xxx"
}
}
]
}
}
# 使用别名查询
$ GET /nginxlogs-read-alias/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
1.2 时间索引的缺点
注意: 虽然使用带时间的索引可以带来很多方便,但是在实际过程中使用带时间的索引也有一定的缺陷。
- 对于写入之后需要数据变更的不是用时间索引
- 直接使用时间分割也可能存在某段时间数据量集中,导致索引分片超过设计容量的问题,可能影响性能
- 索引维护起来比较麻烦(当然可以使用 template 进行管理,前提是满足业务需求)
2. 使用 Rollover 管理索引
Rollover 的原理是使用一个别名指向真正的索引,当指向的索引满足一定条件(文档数或时间或索引大小)更新实际指向的索引。
2.1 创建索引
PUT myro-000001
{
"aliases": {
"myro_write_alias":{}
}
}
2.2 通过别名写入数据
这里使用bulk接口进行写入数据
$ POST /myro_write_alias/_bulk?refresh=true
{"create":{}}
{"name":"xxx"}
{"create":{}}
{"name":"xxx"}
{"create":{}}
{"name":"xxx"}
{
"took" : 37,
"errors" : false,
"items" : [
{
"create" : {
"_index" : "myro-000001",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "wVvFtnIBUTVfQxRWwXyM",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"forced_refresh" : true,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 2,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 0,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"status" : 201
}
},
{
"create" : {
"_index" : "myro-000001",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "wlvFtnIBUTVfQxRWwXyM",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"forced_refresh" : true,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 2,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 1,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"status" : 201
}
},
{
"create" : {
"_index" : "myro-000001",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "w1vFtnIBUTVfQxRWwXyM",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"forced_refresh" : true,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 2,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 2,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"status" : 201
}
}
]
}
2.3 执行 rollover 操作
给索引设置具体的rollover条件,任意一个条件触发都会进行rollover:
下面我们给索引别名设置rollover规则为
-
最大文档数为3
-
分片最大大小为5gb
-
文档最长时间7d
$ POST /myro_write_alias/_rollover { "conditions": { "max_age": "7d", "max_docs": 3, "max_size": "5gb" } } { "acknowledged" : true, "shards_acknowledged" : true, "old_index" : "myro-000001", "new_index" : "myro-000002", "rolled_over" : true, "dry_run" : false, "conditions" : { "[max_docs: 3]" : true, "[max_size: 5gb]" : false, "[max_age: 7d]" : false } }
此时,我们已经设置了 rollover 规则,这个时候尝试继续写入.
$ POST /myro_write_alias/_doc
{"name":"xxx"}
# 发现已经写入新的索引,因为前面已经有三个doc,这次写入触发了rollover规则
{
"_index" : "myro-000002",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "BdbMtnIBgpLCCHbxhihi",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 2,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 0,
"_primary_term" : 1
}
2.4 使用 Rollover 的缺点
- 必须对索引别名先进行
rollover规则设置才可以进行自动 roll - 对于开发者不够友好
3. 使用 ILM(Index Lifecycle Management ) 管理索引
ES 一直在索引管理这块进行优化迭代,从 6.7 版本推出了索引生命周期管理(Index Lifecycle Management ,简称 ILM) 机制,是目前官方提供的比较完善的索引管理方法。所谓 Lifecycle (生命周期) 是把索引定义了四个阶段:
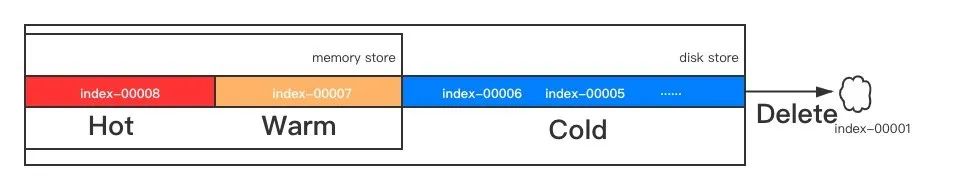
Hot: 索引可写入,也可查询,也就是我们通常说的热数据,为保证性能数据通常都是在内存中的Warm: 索引不可写入,但可查询,介于热和冷之间,数据可以是全内存的,也可以是在 SSD 的硬盘上的Cold: 索引不可写入,但很少被查询,查询的慢点也可接受,基本不再使用的数据,数据通常在大容量的磁盘上Delete: 索引可被安全的删除
这 4 个阶段是 ES 定义的一个索引从生到死的过程,Hot -> Warm -> Cold -> Delete 4 个阶段只有 Hot 阶段是必须的,其他 3 个阶段根据业务的需求可选。
3.1 建立 Lifecycle 策略Kibina 中创建 lifecycle 策略
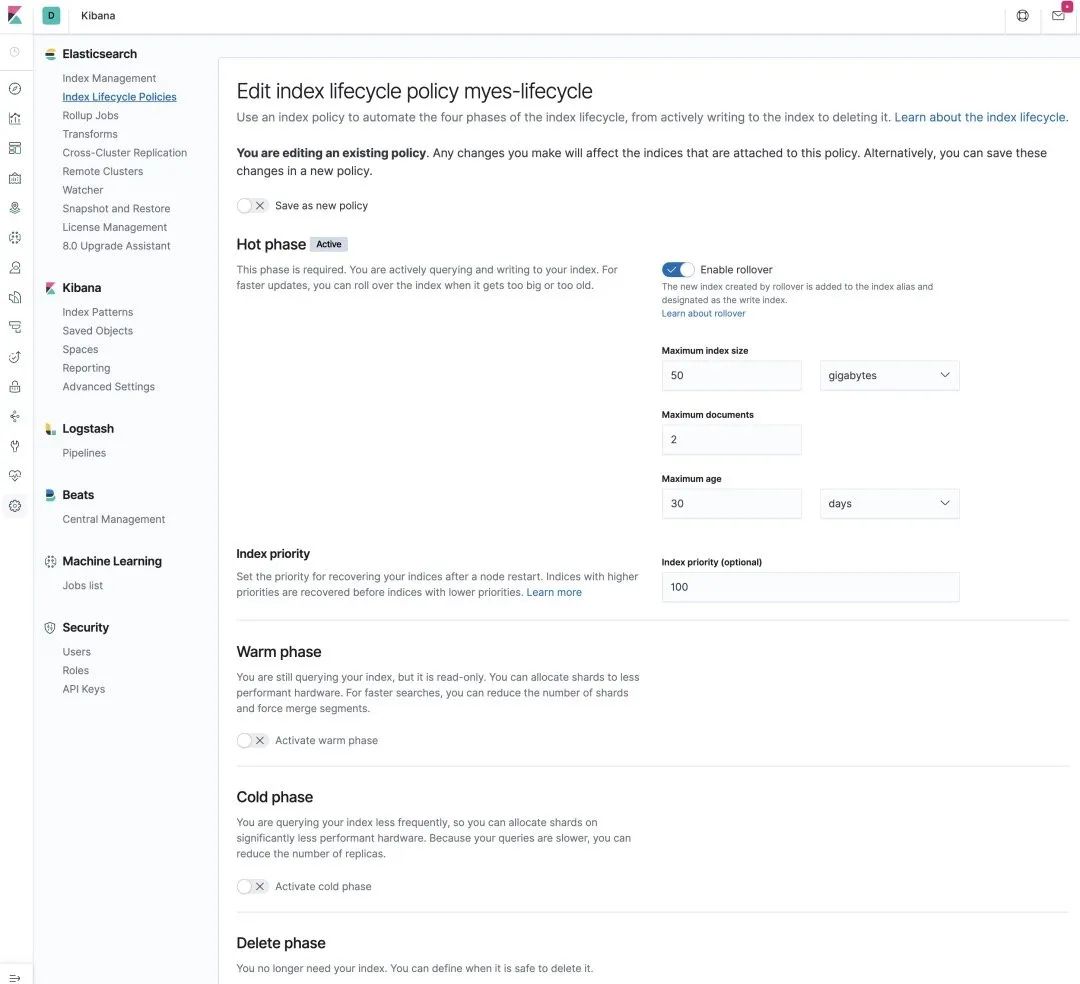
如图,只启用了Hot阶段,并且设置了 rollover 规则。
对应的 HTTP 请求参数如下:
$ PUT _ilm/policy/myindex-lifecycle
{
"policy": {
"phases": {
"hot": {
"min_age": "0ms",
"actions": {
"rollover": {
"max_age": "30d",
"max_size": "50gb",
"max_docs": 2
},
"set_priority": {
"priority": 100
}
}
}
}
}
}
3.2 建立索引模板
$ PUT /_template/myindex_template
{
"index_patterns": [
"myindex-*"
],
"aliases": {
"myindex_reade_alias": {}
},
"settings": {
"index": {
"lifecycle": {
"name": "myindex-lifecycle",
"rollover_alias": "myindex_write_alias"
},
"refresh_interval": "30s",
"number_of_shards": "12",
"number_of_replicas": "1"
}
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
注意:
- 模板匹配以索引前缀开头的索引(myindex-)
- 使用此模板的索引会自动创建
myindex_write_alias的别名,方便数据检索 - 模版绑定了上面创建的 Lifecycle 策略,并且用于 rollover 的别名是
myindex_write_alias
3.3 创建索引
$ PUT /myindex-testindex-000001
{
"aliases": {
"myindex_write_alias":{}
}
}
3.4 查看索引配置
$ GET /myindex-testindex-000001
{
"myindex-testindex-000001" : {
"aliases" : {
"myindex_reade_alias" : { },
"myindex_write_alias" : { }
},
"mappings" : {
"dynamic_templates" : [
{
"message_full" : {
"match" : "message_full",
"mapping" : {
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"ignore_above" : 2048,
"type" : "keyword"
}
},
"type" : "text"
}
}
},
{
"message" : {
"match" : "message",
"mapping" : {
"type" : "text"
}
}
},
{
"strings" : {
"match_mapping_type" : "string",
"mapping" : {
"type" : "keyword"
}
}
}
],
"properties" : {
"name" : {
"type" : "keyword"
}
}
},
"settings" : {
"index" : {
"lifecycle" : {
"name" : "myindex-lifecycle",
"rollover_alias" : "myindex_write_alias"
},
"refresh_interval" : "30s",
"number_of_shards" : "12",
"translog" : {
"sync_interval" : "5s",
"durability" : "async"
},
"provided_name" : "myindex-testindex-000001",
"max_result_window" : "65536",
"creation_date" : "1592222799955",
"unassigned" : {
"node_left" : {
"delayed_timeout" : "5m"
}
},
"priority" : "100",
"number_of_replicas" : "1",
"uuid" : "tPwDbkuvRjKtRHiL4fKcPA",
"version" : {
"created" : "7050199"
}
}
}
}
}
3.5 写入数据
$ POST /myindex_write_alias/_bulk?refresh=true
{"create":{}}
{"name":"xxx"}
{"create":{}}
{"name":"xxx"}
{"create":{}}
{"name":"xxx"}
{
"took" : 18,
"errors" : false,
"items" : [
{
"create" : {
"_index" : "myindex-testindex-000001",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "jF3it3IBUTVfQxRW1Xys",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"forced_refresh" : true,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 2,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 0,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"status" : 201
}
},
{
"create" : {
"_index" : "myindex-testindex-000001",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "jV3it3IBUTVfQxRW1Xys",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"forced_refresh" : true,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 2,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 0,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"status" : 201
}
},
{
"create" : {
"_index" : "myindex-testindex-000001",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "jl3it3IBUTVfQxRW1Xys",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"forced_refresh" : true,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 2,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 0,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"status" : 201
}
}
]
}
3.6 配置 Lifecycle 自动 Rollover 的时间间隔
由于 ElasticSearch 并不是一个 realtime 的的系统,因此很多操作并不能及时生效,因此需要在 lifecycle 中设置时间间隔。而 ElasticSearch 中默认的 ILM 策略的时间间隔为 10min。
# 修改时间间隔
$ PUT _cluster/settings
{
"transient": {
"indices.lifecycle.poll_interval": "3s"
}
}
 51工具盒子
51工具盒子