文章已同步至掘金:https://juejin.cn/post/6844903977541173261
欢迎访问?,有任何问题都可留言评论哦~
在我们使用 React 中,不可避免的要进行组件之间的通信(数据传递)。
需要注意一点:React中数据的流动是单向的
组件之间的数据传递大致分为一下几种:
-
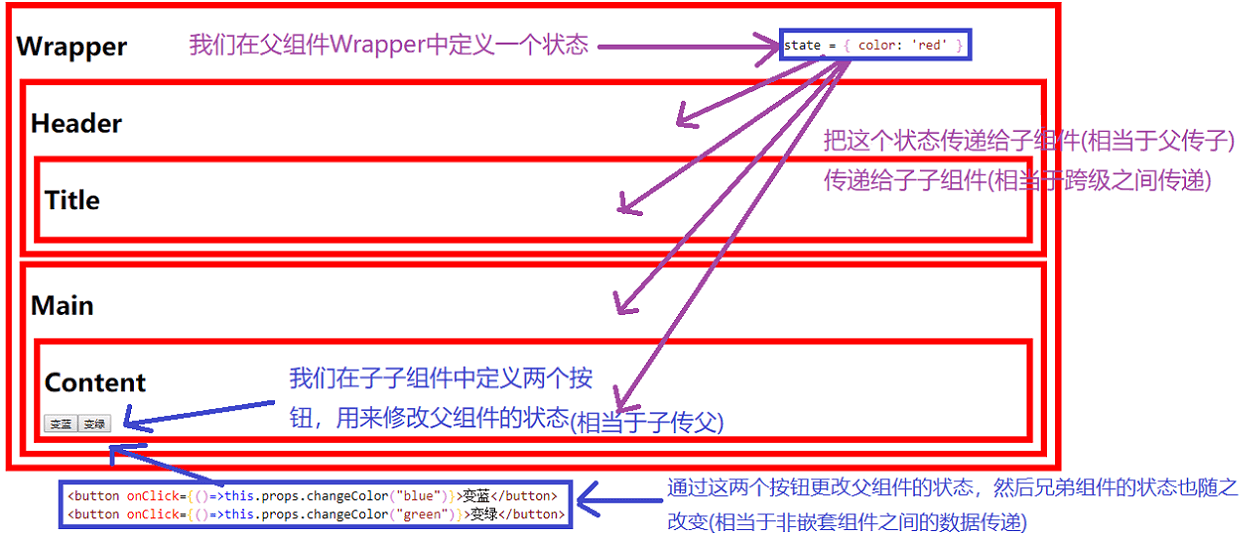
父组件向子组件传递数据
-
子组件向父组件传递数据
-
跨级组件之间传递数据(例如父组件向子子组件传递数据)
-
非嵌套组件之间传递数据
下面我们使用两种方法 (props和context),分别写段代码来实现上面四种通信的方式
整体通信图解:
运行效果:

使用props通信 {#%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8props%E9%80%9A%E4%BF%A1}
直接上代码:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
state = { color: 'red' }
changeColor = color => {
this.setState({ color: color })
}
render() {
return (
<div style={{ border: 8px solid ${this.state.color}, padding: "5px", margin: '5px' }}>
<h1>Wrapper</h1>
<Header color={this.state.color}></Header>
<Main changeColor={this.changeColor.bind(this)} color={this.state.color}></Main>
</div>
)
}
}
class Header extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div style={{ border: 8px solid ${this.props.color}, padding: "5px", margin: '5px' }}>
<h1>Header</h1>
<Title color={this.props.color}></Title>
</div>
)
}
}
class Title extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div style={{ border: 8px solid ${this.props.color}, padding: "5px", margin: '5px' }}>
<h1>Title</h1>
</div>
)
}
}
class Main extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div style={{ border: 8px solid ${this.props.color}, padding: "5px", margin: '5px' }}>
<h1>Main</h1>
<Content changeColor={this.props.changeColor} color={this.props.color}></Content>
</div>
)
}
}
class Content extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div style={{ border: 8px solid ${this.props.color}, padding: "5px", margin: '5px' }}>
<h1>Content</h1>
<button onClick={()=>this.props.changeColor("blue")}>变蓝</button>
<button onClick={()=>this.props.changeColor("green")}>变绿</button>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
图解:

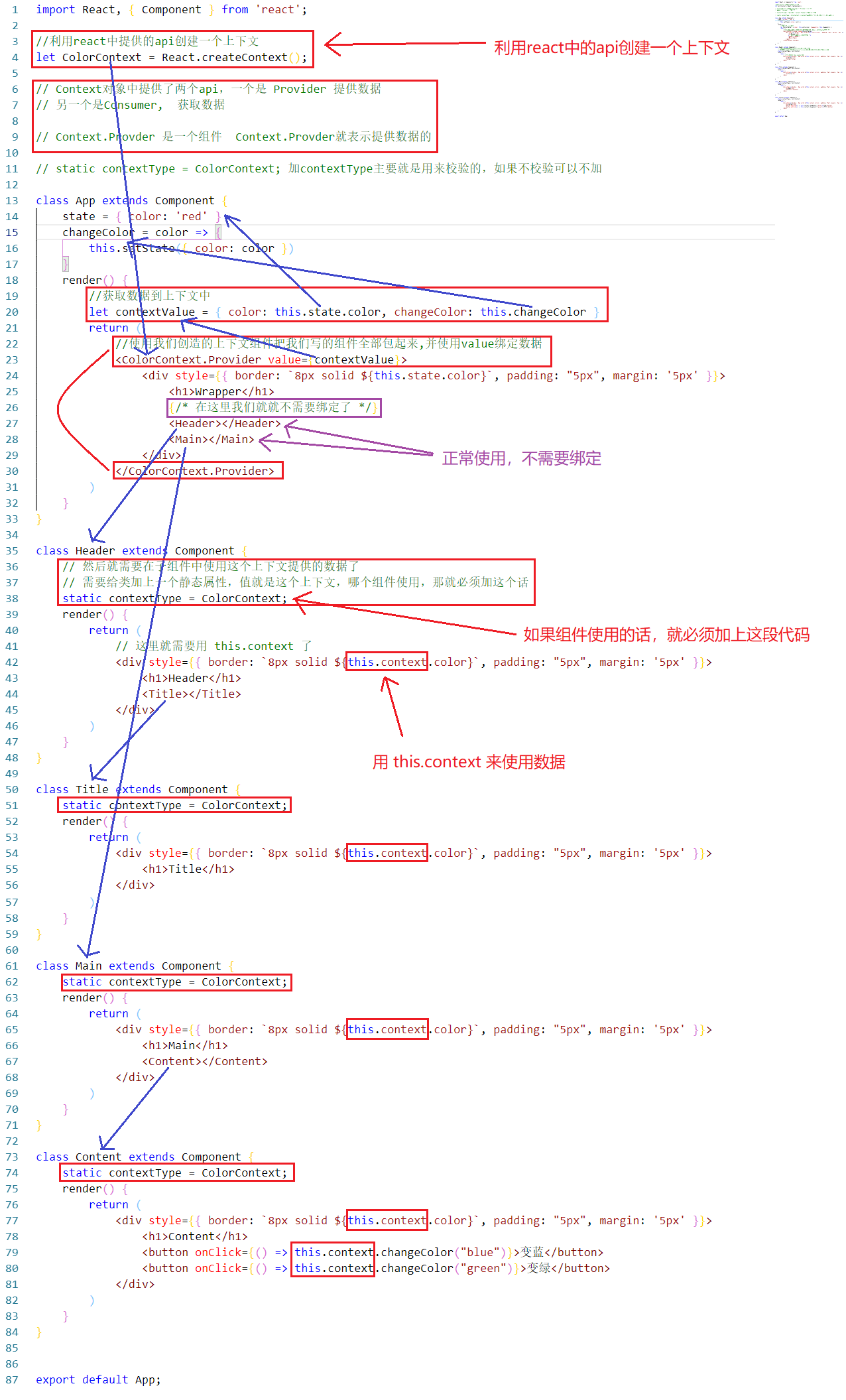
使用context通信 {#%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8context%E9%80%9A%E4%BF%A1}
上面的代码 想必也看到了不足,如果子子组件需要使用父组件的状态,就需要逐级传递在组件中书写传递代码
并且这里面还只是嵌套了两级,组件也比较少,如果组件多,状态多的话怎么办?
套会套会,就把自己给套迷了,所以使用上面方法很容易出现问题,所以在这里我们使用react中给我们提供的api---Context来解决,也就是执行上下文
当然这也不是最优的解决方式,如果是大型项目的话,最好使用Redux来管理我们的状态,如果是小型项目的话,也没必要使用Redux,因为React中自身也提供了状态管理机制
上代码:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
//利用react中提供的api创建一个上下文
let ColorContext = React.createContext();
// Context对象中提供了两个api,一个是 Provider 提供数据
// 另一个是Consumer, 获取数据
// Context.Provder 是一个组件 Context.Provder就表示提供数据的
// static contextType = ColorContext; 加contextType主要就是用来校验的,如果不校验可以不加
class App extends Component {
state = { color: 'red' }
changeColor = color => {
this.setState({ color: color })
}
render() {
//获取数据到上下文中
let contextValue = { color: this.state.color, changeColor: this.changeColor }
return (
//使用我们创造的上下文组件把我们写的组件全部包起来,并使用value绑定数据
<ColorContext.Provider value={contextValue}>
<div style={{ border: 8px solid ${this.state.color}, padding: "5px", margin: '5px' }}>
<h1>Wrapper</h1>
{/* 在这里我们就就不需要绑定了 */}
<Header></Header>
<Main></Main>
</div>
</ColorContext.Provider>
)
}
}
class Header extends Component {
// 然后就需要在子组件中使用这个上下文提供的数据了
// 需要给类加上一个静态属性,值就是这个上下文,哪个组件使用,那就必须加这个话
static contextType = ColorContext;
render() {
return (
// 这里就需要用 this.context 了
<div style={{ border: 8px solid ${this.context.color}, padding: "5px", margin: '5px' }}>
<h1>Header</h1>
<Title></Title>
</div>
)
}
}
class Title extends Component {
static contextType = ColorContext;
render() {
return (
<div style={{ border: 8px solid ${this.context.color}, padding: "5px", margin: '5px' }}>
<h1>Title</h1>
</div>
)
}
}
class Main extends Component {
static contextType = ColorContext;
render() {
return (
<div style={{ border: 8px solid ${this.context.color}, padding: "5px", margin: '5px' }}>
<h1>Main</h1>
<Content></Content>
</div>
)
}
}
class Content extends Component {
static contextType = ColorContext;
render() {
return (
<div style={{ border: 8px solid ${this.context.color}, padding: "5px", margin: '5px' }}>
<h1>Content</h1>
<button onClick={() => this.context.changeColor("blue")}>变蓝</button>
<button onClick={() => this.context.changeColor("green")}>变绿</button>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
图解:
上面是在类组件中使用上下文,那么如果不是类组件,是函数组件呢?该怎么使用context(上下文)
这里我们把Main的类组件换成函数组件:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
let ColorContext = React.createContext();
class App extends Component {
state = { color: 'red' }
changeColor = color => {
this.setState({ color: color })
}
render() {
let contextValue = { color: this.state.color, changeColor: this.changeColor }
return (
<ColorContext.Provider value={contextValue}>
<div style={{ border: 8px solid ${this.state.color}, padding: "5px", margin: '5px' }}>
<h1>Wrapper</h1>
<Header></Header>
<Main></Main>
</div>
</ColorContext.Provider>
)
}
}
class Header extends Component {
static contextType = ColorContext;
render() {
return (
<div style={{ border: 8px solid ${this.context.color}, padding: "5px", margin: '5px' }}>
<h1>Header</h1>
<Title></Title>
</div>
)
}
}
class Title extends Component {
static contextType = ColorContext;
render() {
return (
<div style={{ border: 8px solid ${this.context.color}, padding: "5px", margin: '5px' }}>
<h1>Title</h1>
</div>
)
}
}
// class Main extends Component {
// static contextType = ColorContext;
// render() {
// return (
// <div style={{ border: 8px solid ${this.context.color}, padding: "5px", margin: '5px' }}>
// <h1>Main</h1>
// <Content></Content>
// </div>
// )
// }
// }
function Main() {
return (
//需要使用ColorContext.Consumer包起来
<ColorContext.Consumer>
{
value => (
<div style={{ border: 8px solid ${value.color}, padding: "5px", margin: '5px' }}>
<h1>Main</h1>
<Content></Content>
</div>
)
}
</ColorContext.Consumer>
)
}
class Content extends Component {
static contextType = ColorContext;
render() {
return (
<div style={{ border: 8px solid ${this.context.color}, padding: "5px", margin: '5px' }}>
<h1>Content</h1>
<button onClick={() => this.context.changeColor("blue")}>变蓝</button>
<button onClick={() => this.context.changeColor("green")}>变绿</button>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
事实上,在组件间进行通信时,这些通信方式都可以使用,区别只在于使用相应的通信方式的复杂程度和个人喜好,选择最合适的那一个。
当然,自己实现组件间的通信还是太难以管理了,因此出现了很多状态管理工具,如 redux、mobx 等,使用这些工具使得组件间的通信更容易追踪和管理。
 51工具盒子
51工具盒子