本章的内容基于官方文档编写: https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/reference/html/core.html#spring-core
Spring版本为5.2.9
# (一)Bean的作用域 {#一-bean的作用域}
Spring中Bean的作用域一共有六种
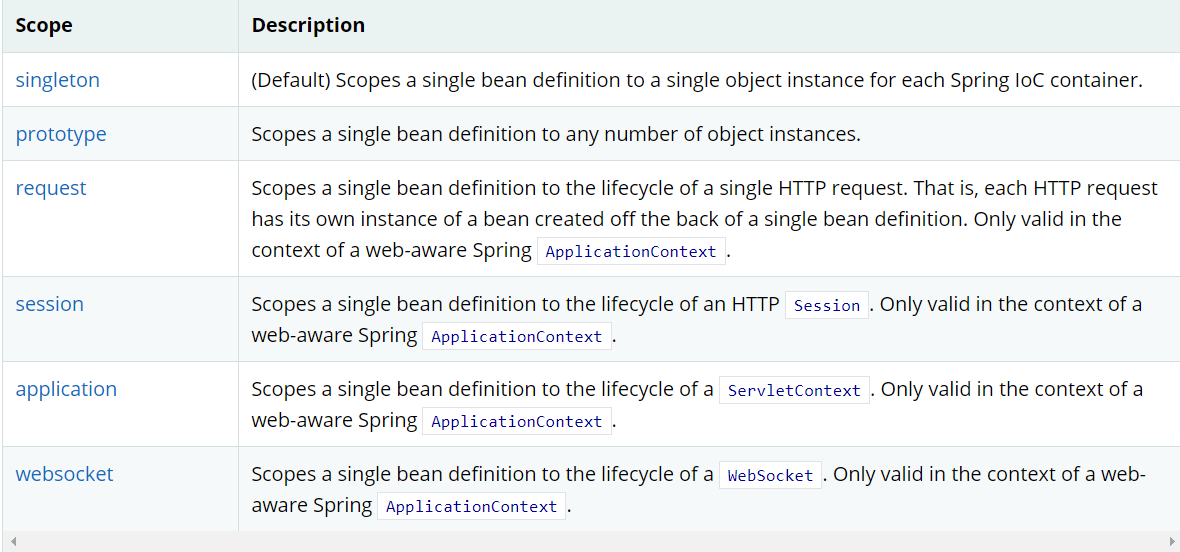
# (1.1)singleton单例作用域 {#_1-1-singleton单例作用域}
spring中的bean默认使用单例作用域,即全局只创建这一个bean对象,在程序中获取到的bean都是同一个。当然也可以显式的配置作用域:
<bean id="user" class="com.javayz.pojo.User" scope="singleton">
# (1.2)prototype原型作用域 {#_1-2-prototype原型作用域}
原型模式是指每次从容器中get一个Bean对象的时候都会产生一个新对象
<bean id="user" class="com.javayz.pojo.User" scope="prototype">
# (1.3)web开发中使用的另外四种作用域 {#_1-3-web开发中使用的另外四种作用域}
request、session、application和websocket只能在web开发中使用,分别表示:
request:bean在一个请求中共用一个。
session:bean在同一个session中共用一个。
application:bean在单个ServletContext中共用一个。
websocket:bean在单个Websocket中共用一个。
# (二)Bean的自动装配 {#二-bean的自动装配}
在之前的内容中,所有的bean都是手动去给其赋值,除了手动赋值外,Bean还支持隐式地自动装配
首先搭建一个简单的例子用于测试:
# 2.1、例子搭建 {#_2-1、例子搭建}
两个实体类:
public class Teacher {
public void teach(){
System.out.println("上课");
}
}
public class Student {
private String name;
private Teacher teacher;
//省略get、set方法
}
bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="teacher" class="com.javayz.pojo.Teacher"/>
<bean id="student" class="com.javayz.pojo.Student">
<property name="name" value="javayz"/>
<property name="teacher" ref="teacher"/>
</bean>
</beans>
测试:
@org.junit.Test
public void test(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
Student student = (Student) context.getBean("student");
student.getTeacher().teach();
}
这是一种手动装配的方式,在bean.xml中,我们给teacher这个变量手动装配了teacher这个id的bean。现在我们使用自动装配:
# 2.2 autowire自动装配 {#_2-2-autowire自动装配}
<bean id="teacher" class="com.javayz.pojo.Teacher"/>
<bean id="student" class="com.javayz.pojo.Student" autowire="byName">
<property name="name" value="javayz"/>
</bean>
在这里我们没有写teacher属性对应哪个bean,而是用了autowire="byName",Spring容器就会自动帮我们根据bean的名称去寻找对应的bean。除了byName后,还有其他的几种方式:
byName:自动在上下文中查找,找到和自己set方法后的值名称相同的bean;
byType:自动在上下文中查找,找到和自己对象类型相同的bean,使用byType需要保证bean全局唯一;
# (三) 使用注解实现自动装配 {#三-使用注解实现自动装配}
使用注解需要我们配置开启:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:annotation-config/>
</beans>
还是上面的这个例子,这次在xml文件中只申明一个bean:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:annotation-config/>
<bean id="teacher" class="com.javayz.pojo.Teacher"/>
<bean id="student" class="com.javayz.pojo.Student"/>
</beans>
在实体类中通过@Autowired注解注入Bean
public class Student {
private String name;
@Autowired
private Teacher teacher;
//省略get、set方法
}
最终实现的效果和手动的注入是一样的。如果你在xml中为同一个类定义了多个bean,则可以使用@Qualifier()指定某个bean:
public class Student {
private String name;
@Autowired
@Qualifier(value = "teacher2")
private Teacher teacher;
}
除了使用@Autowired外,还可以使用@Resocure注解装配bean
public class Student {
private String name;
@Resource
private Teacher teacher;
}
@Autowired和@Resource的区别在于:
@Autowired通过ByName方式实现,如果找不到对象就报空指针异常;
@Resource通过Byname方式实现,如果找不到名字,就通过ByType实现,否则就报错;
 51工具盒子
51工具盒子