systemctl手动配置mysql服务开机自启动
mysql systemctl (mysql加入systemctl 启动)
第一步: 创建文件mysqld.service
进入目录:
/usr/lib/systemd/system/
[root@k8s243 /usr/local/bin]#cat /usr/lib/systemd/system/mysql8.service
[Unit]
Description=Mysql8.0.26
After=network.target
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/startmysql.sh
Restart=on-failure
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
其中的启动脚本用到了startmysql.sh,需要去该目录下把这个文件创建一下,并写入命令
[root@k8s243 /usr/local/bin]#cat startmysql.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo "mysql start ....."
/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqld_safe --defaults-file=/etc/my.cnf
然后赋权
chmod +x startmysql.sh
重新加载
systemctl daemon-reload
启动
systemctl start mysql8
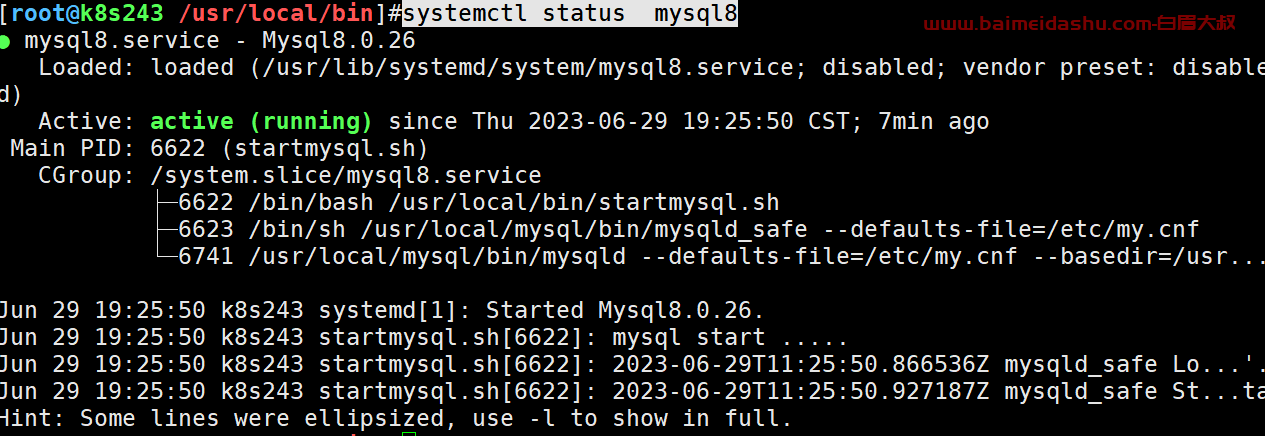
检查:
netstat -tunlp
systemctl status mysql8
补充:
其实不用写单独的脚本也可以的:
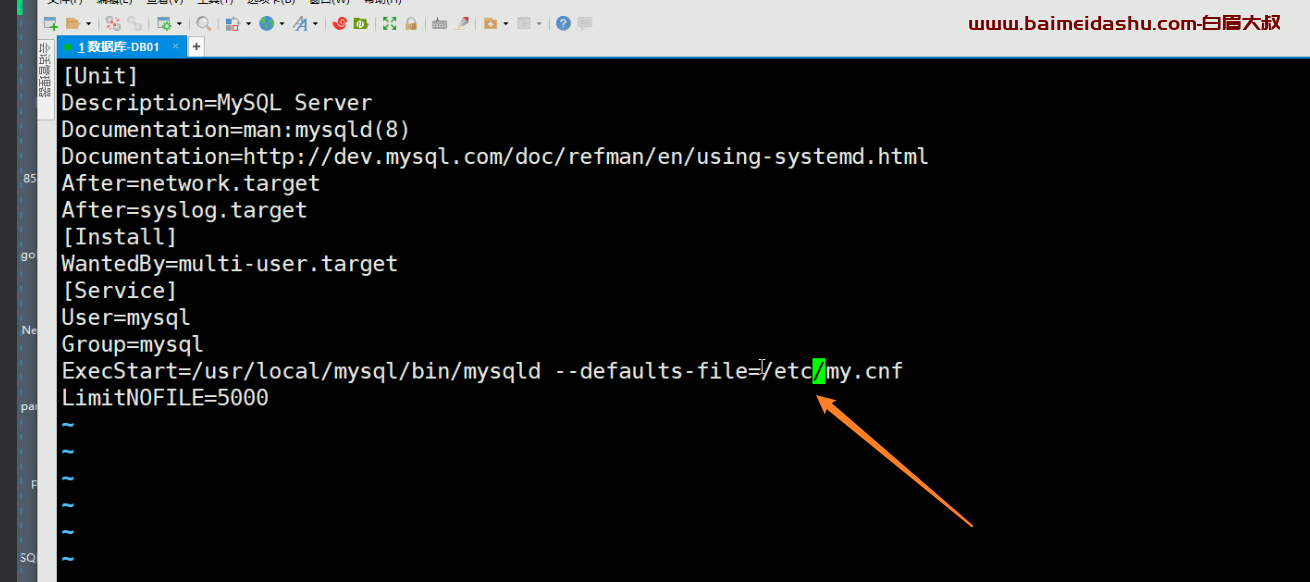
[Unit]
Description=Mysql8.0.26
After=network.target
[Service]
User=mysql
Group=mysql
ExecStart=/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqld --defaults-file=/etc/my.cnf
Restart=on-failure
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
MySQL is a popular open-source relational database management system. systemctl is a command-line tool used in Linux systems with systemd to manage services.
To control the MySQL service using systemctl, you can use the following commands:
-
Start MySQL service:
sudo systemctl start mysql -
Stop MySQL service:
sudo systemctl stop mysql -
Restart MySQL service:
sudo systemctl restart mysql -
Check the status of the MySQL service:
sudo systemctl status mysql -
Enable MySQL service to start on system boot:
sudo systemctl enable mysql -
Disable MySQL service from starting on system boot:
sudo systemctl disable mysql
Please note that the exact name of the MySQL service may vary depending on the Linux distribution you are using.
 51工具盒子
51工具盒子