Docker Hello World
Docker 允许你在容器内运行应用程序,使用docker run命令来在容器内运行一个应用程序。
输出Hello world
先下载一个Centos镜像
文章源自小柒网-https://www.yangxingzhen.cn/7183.html
[root@localhost ~]# docker pull centos
文章源自小柒网-https://www.yangxingzhen.cn/7183.html
Using default tag: latest
文章源自小柒网-https://www.yangxingzhen.cn/7183.html
latest: Pulling from library/centos
文章源自小柒网-https://www.yangxingzhen.cn/7183.html
6910e5a164f7: Pull complete
文章源自小柒网-https://www.yangxingzhen.cn/7183.html
Digest: sha256:4062bbdd1bb0801b0aa38e0f83dece70fb7a5e9bce223423a68de2d8b784b43b
文章源自小柒网-https://www.yangxingzhen.cn/7183.html
Status: Downloaded newer image for centos:latest
文章源自小柒网-https://www.yangxingzhen.cn/7183.html
docker.io/library/centos:latest
文章源自小柒网-https://www.yangxingzhen.cn/7183.html
[root@localhost ~]# docker images
文章源自小柒网-https://www.yangxingzhen.cn/7183.html
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
文章源自小柒网-https://www.yangxingzhen.cn/7183.html
centos latest 831691599b88 3 hours ago 215MB
[root@localhost ~]# docker run centos /bin/echo "Hello world"
Hello world
各个参数解析:
docker:Docker的二进制执行文件。
run:与前面的docker组合来运行一个容器。
centos:指定要运行的镜像,Docker首先从本地主机上查找镜像是否存在,如果不存在,Docker就会从镜像仓库Docker Hub下载公共镜像。
/bin/echo "Hello world":在启动的容器里执行的命令
以上命令完整的意思可以解释为:Docker以centos镜像创建一个新容器,然后在容器里执行bin/echo "Hello world",然后输出结果。
运行交互式的容器
我们通过docker的两个参数 -i -t,让docker运行的容器实现"对话"的能力:
[root@localhost ~]# docker run -it centos /bin/bash
[root@6c75258571be /]#
各个参数解析:
-t:在新容器内指定一个伪终端或终端。
-i:允许你对容器内的标准输入 (STDIN) 进行交互。
注意第二行[root@6c75258571be /]#,此时我们已进入一个centos系统的容器
我们尝试在容器中运行命令 cat /proc/version和ls分别查看当前系统的版本信息和当前目录下的文件列表
[root@6c75258571be /]# cat /proc/version
Linux version 3.10.0-693.el7.x86_64 (builder@kbuilder.dev.centos.org) (gcc version 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-16) (GCC) ) #1 SMP
Tue Aug 22 21:09:27 UTC 2017[root@6c75258571be /]# ls
bin dev etc home lib lib64 lost+found media mnt opt proc root run sbin srv sys tmp usr var
我们可以通过运行 exit 命令或者使用 CTRL+D 来退出容器。
[root@6c75258571be /]# exit
exit
[root@localhost ~]#
注意第三行中[root@localhost ~]# 表明我们已经退出了当期的容器,返回到当前的主机中。
启动容器(后台模式)
使用以下命令创建一个以进程方式运行的容器
[root@localhost ~]# docker run -itd centos /bin/sh -c "while true; do echo hello world; sleep 1; done"
dad8ed873901f6c2810ea77e522a8183f406ea89ad303ac629330c4340e7bab3
在输出中,我们没有看到期望的 "hello world",而是一串长字符
dad8ed873901f6c2810ea77e522a8183f406ea89ad303ac629330c4340e7bab3
这个长字符串叫做容器 ID,对每个容器来说都是唯一的,我们可以通过容器ID 来查看对应的容器发生了什么。
首先,我们需要确认容器有在运行,可以通过docker ps来查看:
[root@localhost ~]# docker ps
输出详情介绍:
CONTAINER ID:容器 ID。
IMAGE:使用的镜像。
COMMAND:启动容器时运行的命令。
CREATED:容器的创建时间。
STATUS:容器状态。
状态有7种:
created(已创建)
restarting(重启中)
running(运行中)
removing(迁移中)
paused(暂停)
exited(停止)
dead(死亡)
PORTS:容器的端口信息和使用的连接类型(tcp\udp)。
NAMES:自动分配的容器名称。
在宿主主机内使用docker logs命令,查看容器内的标准输出:
容器ID
[root@localhost ~]# docker logs dad8ed873901
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
NAMES
[root@localhost ~]# docker logs frosty_bouman
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
停止容器
我们使用docker stop命令来停止容器:
[root@localhost ~]# docker stop dad8ed873901
dad8ed873901为容器ID
[root@localhost ~]# docker stop frosty_bouman
frosty_bouman为NAMES
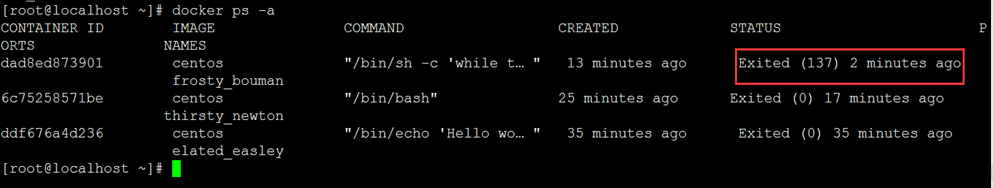
通过docker ps查看,容器已经停止工作:
[root@localhost ~]# docker ps -a
可以看到容器已经不在了。
继续阅读
Docker最后更新:2023-8-21
 51工具盒子
51工具盒子