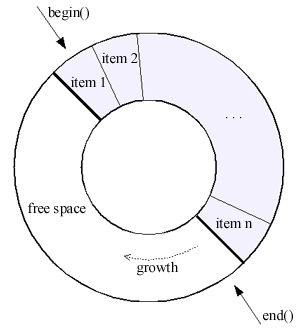
C++ Boost 库中的环形缓冲区(Circular Buffer)是一种数据结构,用于实现固定大小的队列,支持高效的插入和删除操作。它的主要特点是,当缓冲区满时,新的元素会覆盖最旧的元素,从而形成一个环形结构。
- 容器创建 {#title-0} ==================
circular_buffer 提供多种构造容器的方法,主要有:
class circular_buffer
{
private:
//! The internal buffer used for storing elements in the circular buffer.
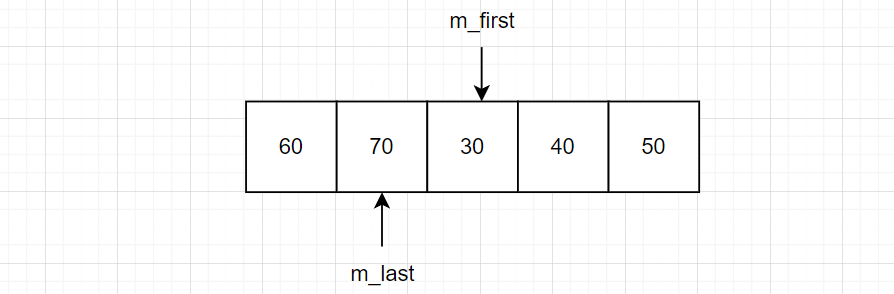
pointer m_buff;
//! The internal buffer's end (end of the storage space).
pointer m_end;
//! The virtual beginning of the circular buffer.
pointer m_first;
//! The virtual end of the circular buffer (one behind the last element).
pointer m_last;
//! The number of items currently stored in the circular buffer.
size_type m_size;
public:
explicit circular_buffer() {}
explicit circular_buffer(capacity_type buffer_capacity) {}
circular_buffer(size_type n, param_value_type item) {}
circular_buffer(capacity_type buffer_capacity, size_type n, param_value_type item) {}
// 拷贝构造函数
circular_buffer(const circular_buffer<T, Alloc>& cb){}
// 移动构造函数
circular_buffer(circular_buffer<T, Alloc>&& cb) {}
template <class InputIterator>
circular_buffer(InputIterator first, InputIterator last) {}
template <class InputIterator>
circular_buffer(capacity_type buffer_capacity, InputIterator first, InputIterator last) {}
};
#if 1
#include <boost/circular_buffer.hpp>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
using namespace boost;
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, circular_buffer<int>& cb)
{
for (auto it = cb.begin(); it != cb.end(); ++it)
cout << *it << " ";
return os;
}
void test()
{
// 容量为0的环形队列
circular_buffer<int> cb1;
// 容量为3的环形队列
circular_buffer<int> cb2(3);
// 容量为3,元素为10
circular_buffer<int> cb3(3, 10);
// 容量为3,前2个元素为10
circular_buffer<int> cb4(3, 2, 10);
/*
c1 capacity:0 size:0 elements:
c2 capacity:3 size:0 elements:
c3 capacity:3 size:3 elements:10 10 10
c4 capacity:3 size:2 elements:10 10
*/
cout << "c1 capacity:" << cb1.capacity() << " size:" << cb1.size() << " elements:" << cb1 << endl;
cout << "c2 capacity:" << cb2.capacity() << " size:" << cb2.size() << " elements:" << cb2 << endl;
cout << "c3 capacity:" << cb3.capacity() << " size:" << cb3.size() << " elements:" << cb3 << endl;
cout << "c4 capacity:" << cb4.capacity() << " size:" << cb4.size() << " elements:" << cb4 << endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}
#endif
- 插入删除 {#title-1} ==================
Boost 中主要使用 push_front、push_back、insert、rinsert 实现元素插入,使用 pop_back、pop_front、erase、clear 实现元素的删除。
#if 1
#include <boost/circular_buffer.hpp>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
using namespace boost;
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, circular_buffer<int>& cb)
{
for (auto it = cb.begin(); it != cb.end(); ++it)
cout << *it << " ";
return os;
}
// 1. push_front、push_back
void test01()
{
circular_buffer<int> cb(3);
cb.push_back(10);
cb.push_back(20);
cb.push_back(30);
// 覆盖最早的元素 10
cb.push_back(40);
cout << cb << endl;
// 插入 100,尾部元素 40 移除
cb.push_front(100);
cout << cb << endl;
// 插入 200,尾部元素 30 移除
cb.push_front(200);
cout << cb << endl;
}
// 2. insert、rinsert
void test02()
{
circular_buffer<int> cb(3);
#if 1
cb.push_back(10);
cb.push_back(20);
cb.push_back(30);
cout << cb << endl;
#endif
// 在 begin 前一位置插入,不会导致元素覆盖
cb.insert(cb.begin(), 100);
cout << cb << endl;
// 会覆盖左侧第一个元素的值
cb.insert(cb.begin(), 200);
cout << cb << endl;
// 在 end 位置插入,导致最早元素被覆盖
cb.insert(cb.end(), 300);
cout << cb << endl;
// 在 begin 位置插入,最新元素会被覆盖
cb.rinsert(cb.begin(), 500);
cout << cb << endl;
// 在最新元素的后面插入,不会导致覆盖
cb.rinsert(cb.end(), 600);
cout << cb << endl;
}
// 3. pop_back、pop_front、erase、clear
void test03()
{
circular_buffer<int> cb(10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
{
cb.push_back(i * 10);
}
// 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
cout << cb << endl;
cb.pop_front();
cb.pop_back();
// 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
cout << cb << endl;
// 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
cb.erase(cb.begin());
cout << cb << endl;
// 20 30 70 80
cb.erase(cb.begin() + 2, cb.end() - 2);
cout << cb << endl;
// 20 30 70
cb.erase_end(1);
cout << cb << endl;
// 70
cb.erase_begin(2);
cout << cb << endl;
cb.clear();
}
int main()
{
test03();
return 0;
}
#endif
- 容量大小 {#title-2} ==================
#if 1
#include <boost/circular_buffer.hpp>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
using namespace boost;
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, circular_buffer<int>& cb)
{
for (auto it = cb.begin(); it != cb.end(); ++it)
cout << *it << " ";
return os;
}
// 1. set_capacity、rset_capacity
void test01()
{
circular_buffer<int> cb(3);
cb.push_back(10);
cb.push_back(20);
cb.push_back(30);
// reserve 空余空间
cout << "capacity:" << cb.capacity() << " size:" << cb.size() << " reserve:" << cb.reserve() << " elements:" << cb << endl;
// 设置容器容量的大小,当新容量小于当前容量,则:
#if 1
// 从末尾移除元素
cb.set_capacity(2);
#else
// 从开头移除元素
cb.rset_capacity(2);
#endif
cout << "capacity:" << cb.capacity() << " size:" << cb.size() << " elements:" << cb << endl;
}
// 2. resize、rresize
void test02()
{
circular_buffer<int> cb(5);
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; ++i)
{
cb.push_back(i * 10);
}
cout << "capacity:" << cb.capacity() << " size:" << cb.size() << " elements:" << cb << endl;
#if 0
// 从缓冲区的末尾调整大小,扩展时在末尾添加元素,缩小时从末尾移除元素
cb.resize(4);
#else
// 从缓冲区的开头调整大小,扩展时在开头添加元素,缩小时从开头移除元素
cb.rresize(4);
#endif
cout << "capacity:" << cb.capacity() << " size:" << cb.size() << " elements:" << cb << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
#endif
- 元素访问 {#title-3} ==================
#if 1
#include <boost/circular_buffer.hpp>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
using namespace boost;
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, circular_buffer<int>& cb)
{
for (auto it = cb.begin(); it != cb.end(); ++it)
cout << *it << " ";
return os;
}
void test()
{
circular_buffer<int> cb(3);
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; ++ i)
{
cb.push_back(i * 10);
}
cout << cb << endl;
// 1. frot、back 访问头尾元素
cb.front() = 100;
cb.back() = 300;
cout << cb << endl;
// 2. [] 和 at
cb[0] = 11;
cb.at(2) = 33;
cout << cb << endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}
#endif
- 其他操作 {#title-4} ==================
#if 1
#include <boost/circular_buffer.hpp>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
using namespace boost;
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, circular_buffer<int>& cb)
{
for (auto it = cb.begin(); it != cb.end(); ++it)
cout << *it << " ";
return os;
}
void print_cb(int* beg, int* end)
{
for (; beg != end; ++beg)
cout << *beg << " ";
cout << endl;
}
// 1. rotate 设置新的首元素
void test01()
{
circular_buffer<int> cb(3);
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; ++i)
{
cb.push_back(i * 10);
}
cout << cb << endl;
cb.rotate(cb.begin() + 1);
cout << cb << endl;
}
// 2. 容器元素的线性性
void test02()
{
circular_buffer<int> cb(5);
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; ++i)
cb.push_back(i * 7);
cout << cb << endl;
// 是否线性
cout << boolalpha << cb.is_linearized() << endl;
// 返回 C 数组指针
int* p_array = cb.linearize();
cout << boolalpha << cb.is_linearized() << endl;
print_cb(p_array, p_array + cb.size());
}
// 2. array_one、array_two
void test03()
{
circular_buffer<int> cb(5);
for (int i = 1; i <= 7; ++i)
{
cb.push_back(i * 10);
}
cout << cb << endl;
// 30 40 50 60 70
pair<int*, size_t> ret1 = cb.array_one();
pair<int*, size_t> ret2 = cb.array_two();
print_cb(ret1.first, ret1.first + ret1.second);
print_cb(ret2.first, ret2.first + ret2.second);
}
int main()
{
test02();
return 0;
}
#endif
 51工具盒子
51工具盒子