内置对象
JavaScript中的对象分为3种:自定义对象、内置对象、浏览器对象
前面两种对象是JS基础内存,属于ECMAScript,第三种浏览器对象属于我们JS独有的。
内置对象就是指JS语言自带的一些对象,这些对象供开发者使用,并提供了一些常用的或是最基本而必要的功能(属性和方法)。
内置对象最大的优点就是帮助我们快速开发
JavaScript提供了多个内置对象:Math、Date、Array、String等
查询MDN文档
学习一个内置对象的使用,只要学会其常用成员的使用即可。
我们可以通过查文档学习:MDN和W3C
Mozilla开发者网络(MDN)提供了有关开放网络技术(Open Web)的信息,包括HTML、CSS和万维网以及HTML5应用的API。
MDN:https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/
学习对象中的方法
1.查阅方法的功能

2.查阅里面参数的意义和类型

3.查看返回值的意义和类型

4.通过demo进行测试
Math对象
Math数学对象,不是一个构造函数,所以我们不需要new来调用,而是直接使用里面的属性和方法即可,跟数学相关的运算(求绝对值,取整、最大值等)可以使用Math中的成员。
console.log(Math.PI); //一个属性,圆周率
console.log(Math.max(1, 98, 26)); //输出最大值98
console.log(Math.max(1, 98, '岳泽以')); //NaN 如果有任一参数不能被转换为数值,则结果为 NaN。
console.log(Math.max()); //-Infinity 如果没有参数,则结果为 - Infinity。
案例:封装自己的数学对象
利用对象封装自己的数学对象,里面有PI最大值和最小值
var myMath = {
PI: 3.141592653,
max: function() {
var max = arguments[0];
for (var i = 1; i < arguments.length; i++) {
if (arguments[i] > max) {
max = arguments[i];
}
}
return max;
},
min: function() {
var min = arguments[0];
for (var i = 1; i < arguments.length; i++) {
if (arguments[i] < min) {
min = arguments[i];
}
}
return min;
}
}
console.log(myMath.PI);
console.log(myMath.max(1, 5, 8));
console.log(myMath.min(1, 5, 8));
Math绝对值和三个取整方法
Math中的常用成员:
| 成员 | 属性 | |-----------------------|---------------------| | Math.PI | 圆周率 | | Math.floor() | 向下取整 | | Math.ceil() | 向上取整 | | Math.round() | 四舍五入(就近取整)-3.5结果是-3 | | Math.abs() | 绝对值 | | Math.max()/Math.min() | 求最大值和最小值 |
绝对值方法
console.log(Math.abs(1)); //1
console.log(Math.abs(-1)); //1
console.log(Math.abs('-1')); //隐式转换,会把字符串型-1转换为数字型
console.log(Math.abs('zeyi')); //NaN
三个取整方法
1.Math.floor() 向下取整,往最小了取值
console.log(Math.floor(1.1)); //1
console.log(Math.floor(1.9)); //1
2.Math.ceil() 向上取整,往最大了取值
console.log(Math.ceil(1.1)); //2
console.log(Math.ceil(1.9)); //2
3.Math.round(() 四舍五入
console.log(Math.round(1.5)); //2
console.log(Math.round(1.2)); //1
console.log(Math.round(-1.1)); //-1
console.log(Math.round(-1.5)); //-1
注意:其他数字都是四舍五入,但是.5特殊,它往大了取,比如-1.5取-1而不取-2是因为-1>-2。
Math随机数方法
Math对象随机数方法:random() 返回一个随机的小数
返回的随机小数范围:0 =< x < 1
console.log(Math.random());//随机一个小数,刷新变化
我们想要得到俩个数之间的随机整数,并且包含这2个整数
//Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min + 1)) + min;
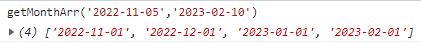
function getRandom(min, max) {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min + 1)) + min;
}
console.log(getRandom(1, 10));
随机点名:
function getRandom(min, max) {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min + 1)) + min;
}
var arr = ['张三', '李四', '王五'];
console.log(arr[getRandom(0, arr.length - 1)]);
日期对象
Date()日期对象是一个构造函数,必须使用new来调用创建我们的日期对象。
使用Date
var date = new Date();
console.log(date);
参数常用写法:
数字型:2022,10,09
var date1 = new Date(2022, 04, 09);
console.log(date1);//返回值大一月
字符串型:'2022-10-09 8:8:8' (常用写法)
var date2 = new Date('2022-04-09 8:8:8');
console.log(date2);
注意:
- Date对象和Math对象不一样,他是一个构造函数,所以我们需要实例化后才能使用。
- Date实例用来处理日期和时间。
- Date获取当前时间必须实例化,如果没有参数,返回当前系统的当前时间。
- 如果括号里面有时间,就返回参数里面的时间。
日期格式化
| 方法名 | 说明 | 代码 | |---------------|------------|--------------------| | getFullYear() | 获取当年 | dObj.getFullYear() | | getMonth() | 获取当月(0-11) | dObj.getMonth() | | getDate() | 获取当天日期 | dObj.getDate() | | getDay() | 获取星期几(0-6) | dObj.getDay() | | getHours() | 获取当前小时 | dObj.getHours() | | getMinutes() | 获取当前分钟 | dObj.getMinutes() | | getSeconds() | 获取当前秒钟 | dObj.getSeconds() |
//单个格式化
var date = new Date();
console.log(date.getFullYear()); //返回当前日期的年
console.log(date.getMonth()); //返回的月份小一个月
console.log(date.getDate()); //返回的是几号
console.log(date.getDay()); //周一返回的是1 周六返回6 周日返回0
格式化为 2022 年 4 月 9 日 星期六:
var year = date.getFullYear();
var month = date.getMonth() + 1;
var dates = date.getDate();
var arr = ['星期日', '星期一', '星期二', '星期三', '星期四', '星期五', '星期六'];
var day = date.getDay();
console.log('今天是:' + year + '年' + month + '月' + dates + '日' + arr[day]);
格式化时分秒:
//单个格式化
var date = new Date();
console.log(date.getHours()); //时
console.log(date.getMinutes()); //分
console.log(date.getSeconds()); //秒
//封装格式为 08:08:00
function getTimes() {
var h = date.getHours();
h = h < 10 ? '0' + h : h;
var m = date.getMinutes();
m = m < 10 ? '0' + m : m;
var s = date.getSeconds();
s = s < 10 ? '0' + s : s;
return h + ':' + m + ':' + s;
}
console.log(getTimes());
时间戳
获取日期的总的毫秒数(时间戳),不是当前时间的毫秒数,而是距离1970年1月1日过了多少毫秒数。
var date = new Date();
console.log(date.valueOf());
//或者
console.log(date.getTime());
//简单写法(最常用的方法)
var date1 = +new Date();
console.log(date1);
//更简单方法,H5新增的
console.log(Date.now());
 51工具盒子
51工具盒子