为了解决特定问题而进行的学习是提高效率的最佳途径。这种方法能够使我们专注于最相关的知识和技能,从而更快地掌握解决问题所需的能力。
(以下练习题来源于《统计学---基于Python》。请在Q群455547227下载原始数据。)
练习题
下表是某只股票连续35个交易日的收盘价格(前3行和后3行)。

(1)分别采用m=5和m=10对收盘价格进行平滑,并绘制实际值和平滑值的图形进行比较。
(2)分别采用以下方法进行预测,并绘制预测图和残差图,对结果进行比较。
-
(a)简单指数平滑和Holt指数平滑;
-
(b)一元线性回归和指数曲线;
-
(c)二阶曲线和三阶曲线。
图形绘制与分析
本文就(2b)题展开分析。 (2b)收盘价的一元线性回归预测 线性趋势(linear trend)是时间序列按一个固定的常数(不变的斜率)增长或下降。时间序列为线性趋势时,除了可以用Holt指数平滑模型进行预测外,还可以使用一元线性回归模型进行预测。 建立一元线性回归模型* * * * * * *
import pandas as pdfrom statsmodels.formula.api import olsdf = pd.read_csv('exercise11_1.csv')
#拟合一元线性回归模型(l_model)l_model = ols('收盘价 ~ 时间', data = df).fit()print(l_model.summary()) # 输出模型结果
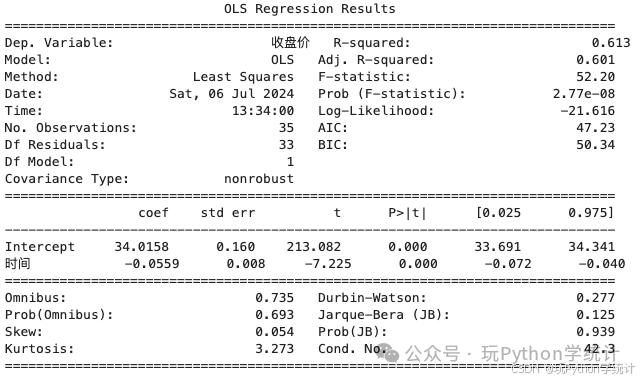
由以上结果得到一元线性回归方程为:Yt=34.0158+(-0.0559)t。决定系数R2=61.3%,F检验的P=2.77e-08,表示模型显著。b1=-0.0559 ,表示时间每变动一期,收盘价平均变动-0.0559。
绘制预测图和残差图* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
# 绘制预测图和残差图import matplotlib.pyplot as pltplt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['Songti SC']plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = Falsedf = pd.read_csv('exercise11_1.csv')#拟合一元线性回归模型(l_model)l_model = ols('收盘价 ~ 时间', data = df).fit()df_pre = pd.DataFrame({'时间':df['时间'], '收盘价':df['收盘价'], '预测值':l_model.fittedvalues, '预测残差':l_model.resid})
# 图(a)预测图plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize = (11, 4))plt.subplot(121)l1 = plt.plot(df_pre['收盘价'], marker = 'o')l2 = plt.plot(df_pre['预测值'], marker = '*', linewidth = 1, markersize = 8, ls = '-.')plt.axvline(34, ls = '--', c = 'grey', linewidth = 1)plt.xticks(range(0, 35, 2), df_pre['时间'][::2])plt.xlabel('时间', size = 12)plt.ylabel('收盘价', size = 12)plt.legend(['收盘价', '预测值'], prop = {'size':11})plt.title('(a)收盘价的一元线性回归预测', size = 13)
# 图(b)残差图plt.subplot(122)res = l_model.resid # 计算残差plt.scatter(range(len(res)), res, marker = 'o', linewidth = 1)plt.hlines(0, 0, 35, linestyle = '--', color = 'red', linewidth = 1)plt.xlabel('时间', size = 12)plt.xticks(range(0, 35, 2), df_pre['时间'][::2])plt.ylabel('残差', size = 12)plt.title('(b)一元线性回归预测残差', size = 13)
plt.tight_layout()
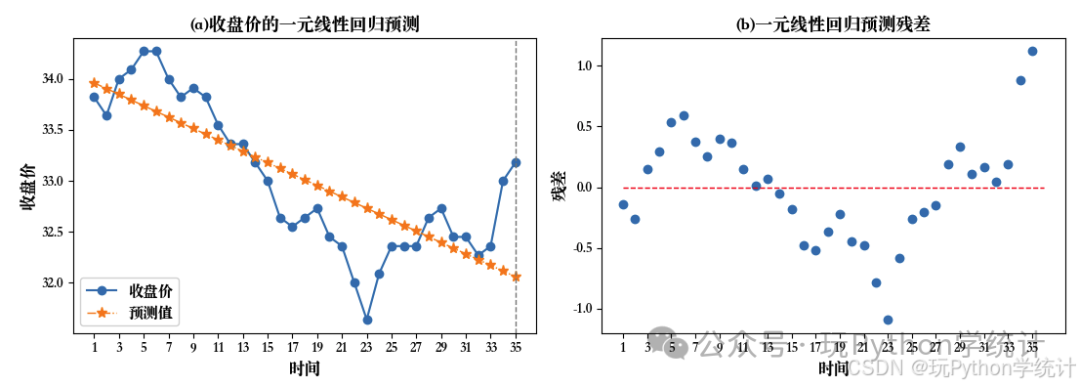
左图展示了收盘价的实际值和预测值,拟合结果并不理想。右图显示,残差围绕0轴分布,但呈现出了有规律的分布,表明所选的模型是不合适的。
(2b)收盘价的指数曲线预测
指数曲线(exponential curve)用于描述以几何级数递增或递减的现象,即时间序列的观测值Yt按指数规律变化,或者说逐期观测值按一定的增长率增长或衰减。
建立指数曲线模型* * * * * * * * * * *
import pandas as pdimport numpy as npfrom statsmodels.formula.api import olsimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltplt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['Songti SC']plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = Falsedf = pd.read_csv('exercise11_1.csv')
# 拟合指数曲线模型(e_model)e_model = ols('np.log(收盘价) ~ 时间', data = df).fit()print(e_model.summary()) # 输出模型结果
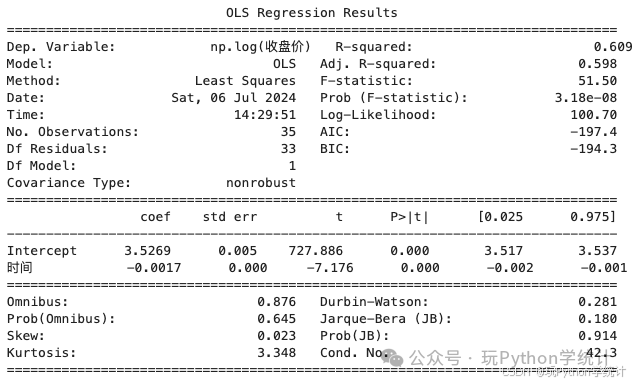
由以上结果得到指数曲线的方程为:Yt=3.5269exp(-0.0017t)。决定系数R2=60.9%,F检验的P=3.18e-08,表示模型显著。b1=-0.0017 ,表示时间每变动一期,收盘价平均变动-0.0017。
绘制预测图和残差图* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
# 绘制预测图和残差图import matplotlib.pyplot as pltplt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['Songti SC']plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = Falsedf = pd.read_csv('exercise11_1.csv')# 拟合指数曲线模型(e_model)e_model = ols('np.log(收盘价) ~ 时间', data = df).fit()df_pre = pd.DataFrame({'时间':df['时间'], '收盘价':df['收盘价'], '预测值':np.exp(e_model.fittedvalues)})# df_pre = df_pre.astype({'时间':int})
# 图(a)预测图plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize = (11, 4))plt.subplot(121)l1 = plt.plot(df_pre['收盘价'], marker = 'o')l2 = plt.plot(df_pre['预测值'], marker = '*', linewidth = 1, markersize = 8, ls = '-.')plt.axvline(34, ls = '--', c = 'grey', linewidth = 1)plt.xticks(range(0, 35, 2), df_pre['时间'][::2])plt.xlabel('时间', size = 12)plt.ylabel('收盘价', size = 12)plt.legend(['收盘价', '预测值'], prop = {'size':11})plt.title('(a)收盘价的指数曲线预测', size = 13)
# 图(b)残差图plt.subplot(122)df_pre['残差'] = df_pre['收盘价'] - df_pre['预测值'] # 计算残差plt.scatter(range(len(df_pre['残差'])), df_pre['残差'], marker = 'o', linewidth = 1)plt.hlines(0, 0, 35, linestyle = '--', color = 'red', linewidth = 1)plt.xlabel('时间', size = 12)plt.xticks(range(0, 35, 2), df_pre['时间'][::2])plt.ylabel('残差', size = 12)plt.title('(b)指数曲线预测残差', size = 13)
plt.tight_layout()
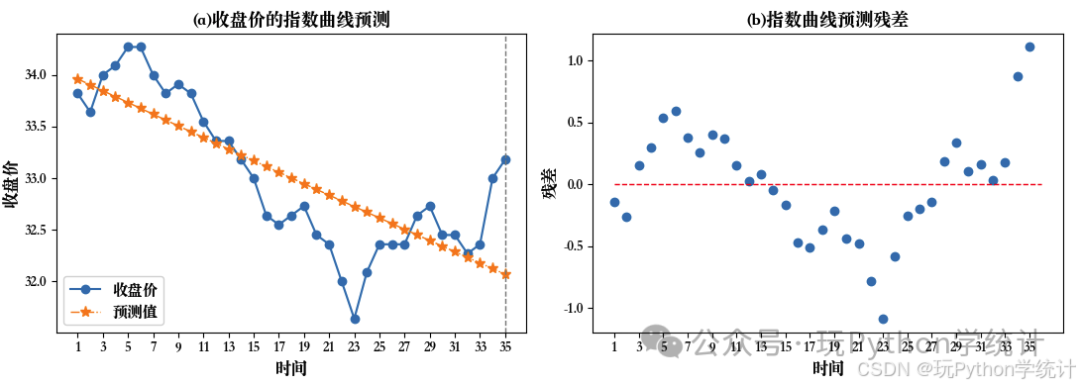
左图展示了收盘价的实际值和预测值,拟合结果不理想。右图显示,残差围绕0轴分布,但呈现出了有规律的分布,表明所选的模型也是不合适的。
 51工具盒子
51工具盒子