* PyMysql
1.PyMysql简介
* 概述
* 它是一个第三方包, 主要用于实现: 通过Python代码, 操作MySQL数据库的.
* 环境搭建
* **方式1: 导包时, 自动安装.**
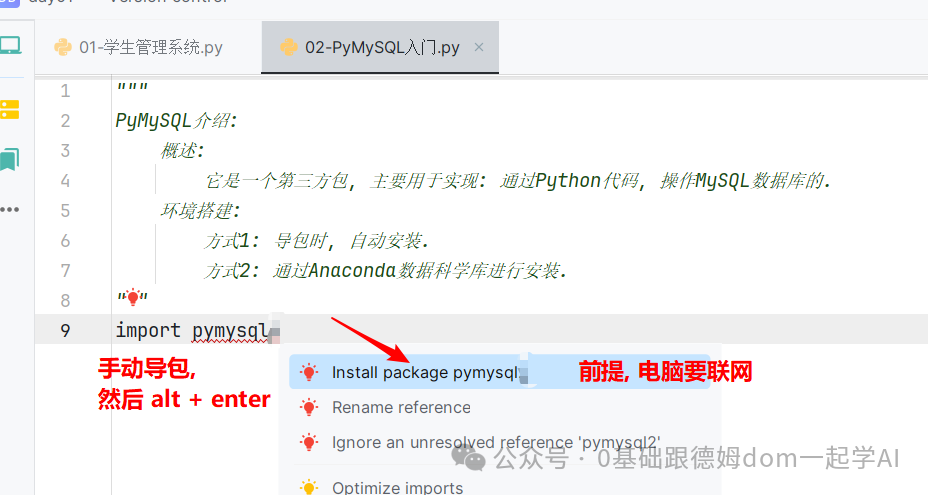
* **方式2: 通过Anaconda数据科学库进行安装.**
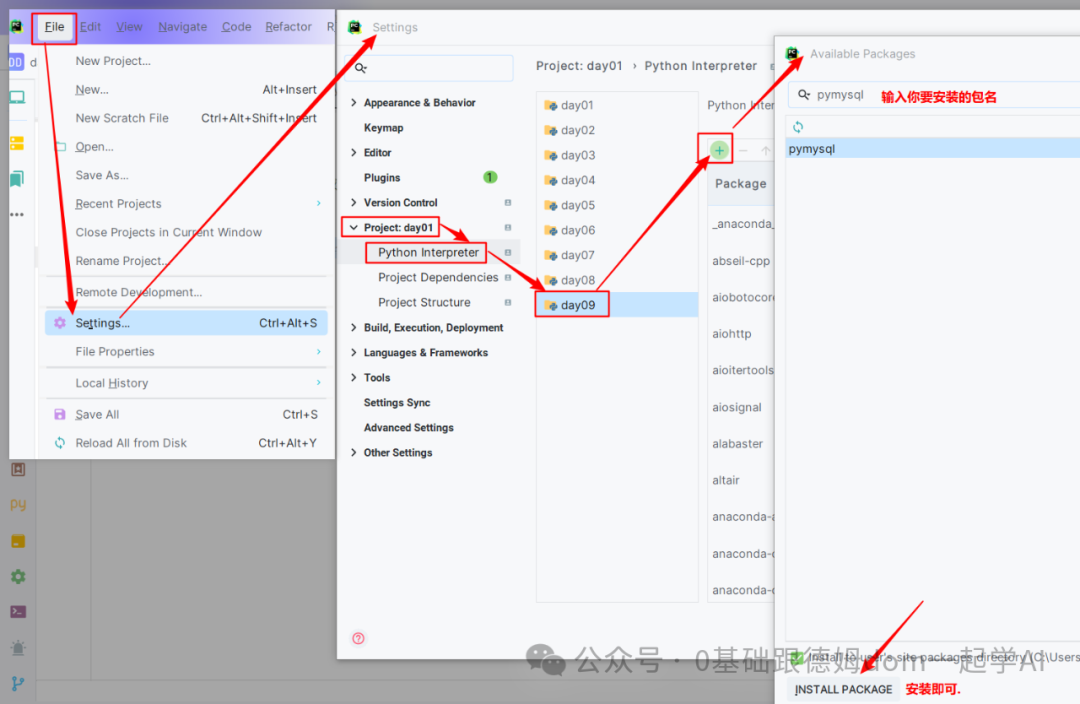
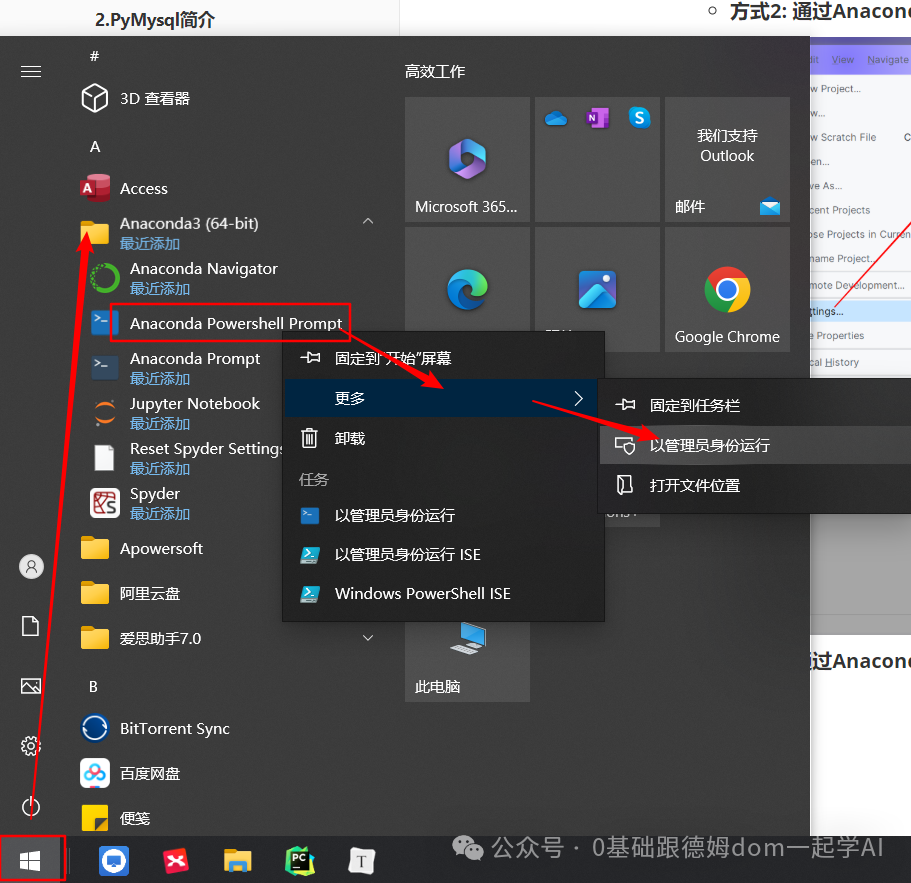
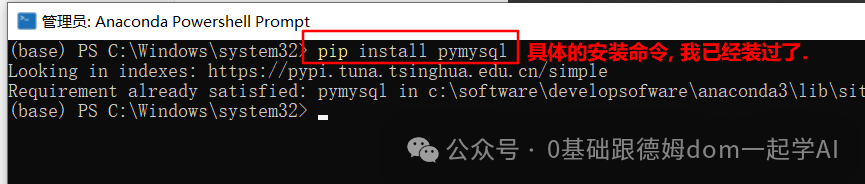
* **方式3: 通过Anaconda的PowerShell窗口, 以管理员的身份运行, 并安装**
* 推荐方式
2.PyMysql-入门代码
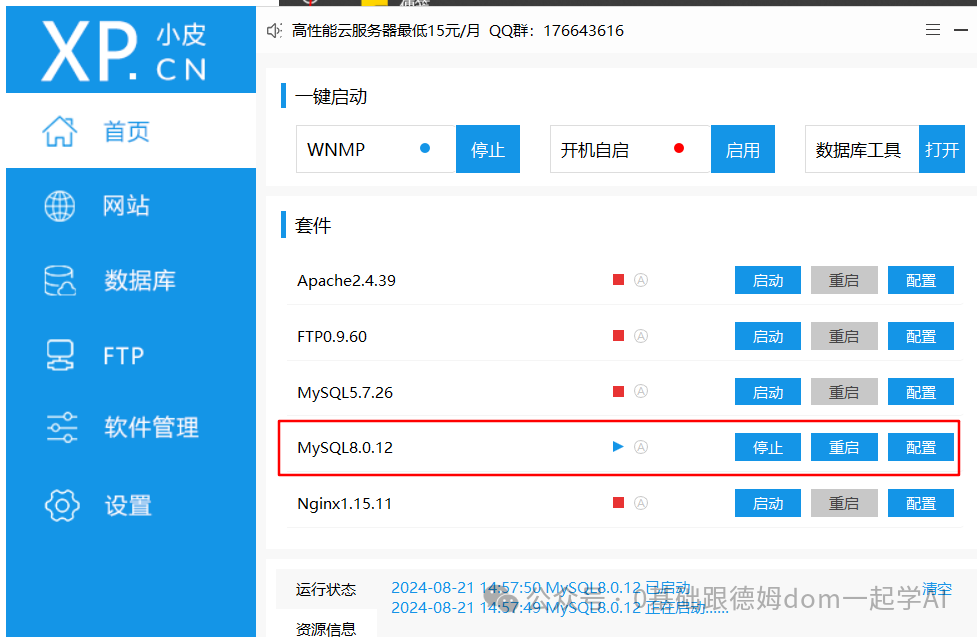
- 启动小皮, 开启MySQL8.X, 或者 MySQL5.X服务.
- 配置PyCharm连接MySQL.
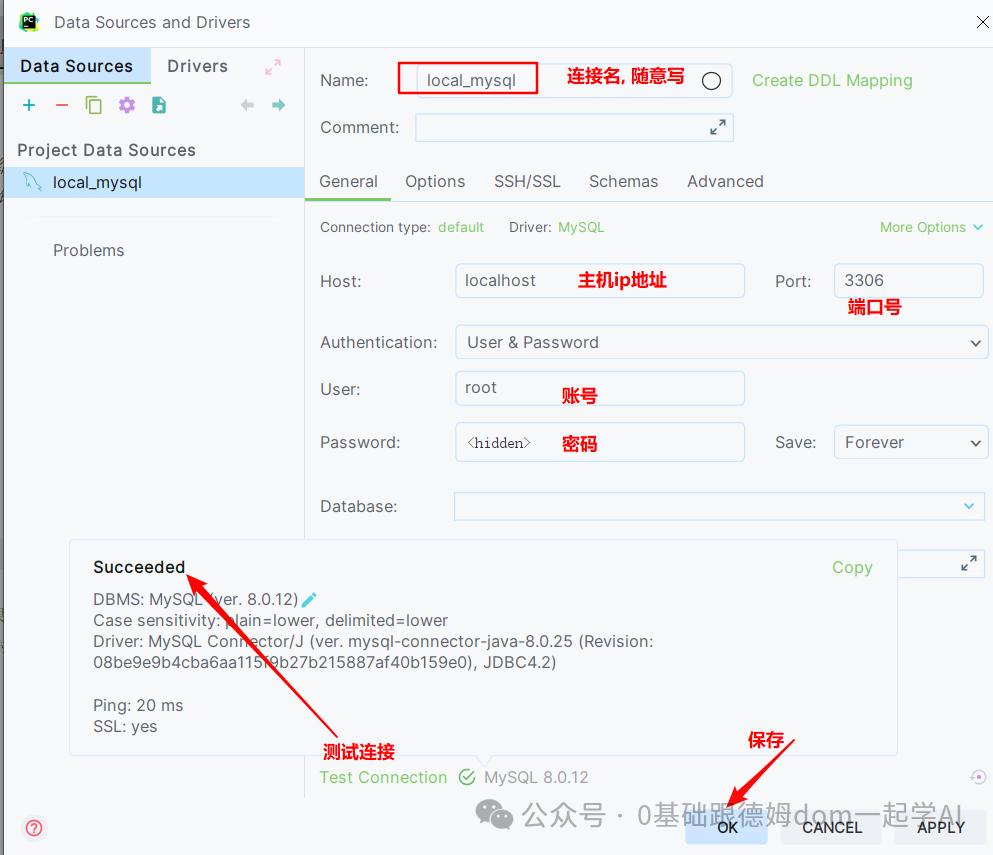
- 查看MySQL中有哪些数据库, 及 准备数据.
```sql
-- 查看所有的数据库.
show databases ;
-- 建库, 切库
create database day09 charset 'utf8';
use day09;
-- 查看所有的数据表
show tables;
-- 建表, 添加表数据.
create table student(
id int primary key auto_increment, # id, 主键自增.
name varchar(20), # 学生姓名.
gender varchar(10) # 学生性别
);
-- 添加表数据
insert into student values(null, '乔峰', '男'), (null, '虚竹', '男'), (null, '王语嫣', '女');
-- 查看表数据.
select * from student;
```
- PyMySQL-入门代码
```python
"""
PyMySQL介绍:
概述:
它是一个第三方包, 主要用于实现: 通过Python代码, 操作MySQL数据库的.
环境搭建:
方式1: 导包时, 自动安装.
方式2: 通过Anaconda数据科学库进行安装.
方式3: 通过Anaconda的PowerShell窗口, 以管理员的身份运行, 并安装
操作步骤:
-
获取连接对象.
-
获取游标对象.
-
执行SQL语句, 获取结果集.
[加一步: 提交事务, 只针对于更新语句(增删改)有效]
-
操作结果集.
-
释放资源.
"""
导包.
import pymysql
main
if name == 'main':
- 获取连接对象. ==========
conn = pymysql.connect(
host='localhost', # 主机地址, 默认是本机, 可以写localhost 或者 127.0.0.1
port=3306, # 端口号
user='root', # 账号
password='123456', # 密码
database='day09', # 要连接到的数据库名称
charset='utf8' # 码表
)
print(conn)
- 获取游标对象. ==========
cursor = conn.cursor()
- 执行SQL语句, 获取结果集. ==================
sql = 'select * from student;'
执行SQL语句.
cursor.execute(sql)
获取结果集, 即: 把每行数据封装成元组, 然后整体放到1个元组中, 即: 元组嵌套元组的形式.
results = cursor.fetchall()
- 操作结果集. =========
print(type(results))
print(results)
- 释放资源. ========
cursor.close()
conn.close()
```
4.PyMysql-查询相关的函数介绍
```python
"""
PyMysql 查询 相关的函数, 即: cursor(游标对象)的函数
fetchall() 获取(查询)SQL语句的所有内容, 每行数据会封装成1个元组, 然后再把所有数据封装到1个元组中, 即: 元组嵌套元组的形式.
fetchmany(n) 一次读取n条数据, 不写默认读取 1条 数据.
fetchone() 一次获取(第)一条数据.
"""
导包.
import pymysql
main
if name == 'main':
- 获取连接对象. ==========
conn = pymysql.connect(
host='localhost', # 主机地址, 默认是本机, 可以写localhost 或者 127.0.0.1
port=3306, # 端口号
user='root', # 账号
password='123456', # 密码
database='day09', # 要连接到的数据库名称
charset='utf8' # 码表
)
print(conn)
- 获取游标对象. ==========
cursor = conn.cursor()
- 执行SQL语句, 获取结果集. ==================
sql = 'select * from student;'
执行SQL语句.
cursor.execute(sql)
获取结果集, 即: 把每行数据封装成元组, 然后整体放到1个元组中, 即: 元组嵌套元组的形式.
results = cursor.fetchall() # 一次获取所有的数据.
results = cursor.fetchmany() # 不写数量, 默认: 一次读取一条数据.
results = cursor.fetchmany(2) # 读取(前)2条数据.
results = cursor.fetchone() # 一次读取(第)一条数据
- 操作结果集. =========
print(type(results))
print(results)
- 释放资源. ========
cursor.close()
conn.close()
```
5.PyMysql-CURD操作-增
```python
"""
案例: 演示PyMysql的 CURD(增删改查)操作.
回顾, PyMysql的核心步骤:
-
获取连接对象.
-
获取游标对象.
-
执行SQL语句, 获取结果集.
-
提交事务, 只针对于 更新语句(增删改) 有效.
-
操作结果集.
-
释放资源.
细节:
-
PyMysql操作SQL语句, 如果是 查询操作, 则: 需要通过 fetchall(), fetchone(), fetchmany(n) 来获取数据.
-
PyMysql操作SQL语句, 如果是 更新操作(增删改), 则: 直接返回的是 受影响的函数.
-
PyMysql操作更新语句, 则: 必须提交事务, 结果才会写到 数据库中.
"""
import pymysql
PyMysql 增
def fun01():
- 获取连接对象. 主机地址 端口号 账号 密码 要连接到的数据库名 码表 ======================================
conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3306, user='root', password='123456', database='day09', charset='utf8')
print(conn)
- 获取游标对象. ==========
cursor = conn.cursor()
- 执行SQL语句, 获取结果集. ==================
sql = "insert into student values(null, '刘亦菲', '女'), (null, '赵丽颖', '女');"
result = cursor.execute(sql) # 返回的是 受影响的行数
print(f"受影响的行数: {result}")
- 提交事务, 只针对于 更新语句(增删改) 有效. ===========================
conn.commit()
- 操作结果集. =========
print('添加成功!' if result > 0 else '添加失败!')
- 释放资源. ========
cursor.close()
conn.close()
PyMysql 删
def fun02():
pass
PyMysql 改
def fun03():
pass
PyMysql 查
def fun04():
pass
在main方法中测试.
if name == 'main':
调用 fun01() 函数, 实现: PyMysql 增 的功能演示.
fun01()
```
6.PyMysql-CURD操作-完整版
```python
"""
案例: 演示PyMysql的 CURD(增删改查)操作.
回顾, PyMysql的核心步骤:
-
获取连接对象.
-
获取游标对象.
-
执行SQL语句, 获取结果集.
-
提交事务, 只针对于 更新语句(增删改) 有效.
-
操作结果集.
-
释放资源.
细节:
-
PyMysql操作SQL语句, 如果是 查询操作, 则: 需要通过 fetchall(), fetchone(), fetchmany(n) 来获取数据.
-
PyMysql操作SQL语句, 如果是 更新操作(增删改), 则: 直接返回的是 受影响的函数.
-
PyMysql操作更新语句, 则: 必须提交事务, 结果才会写到 数据库中.
"""
import pymysql
PyMysql 增
def fun01():
- 获取连接对象. 主机地址 端口号 账号 密码 要连接到的数据库名 码表 ======================================
conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3306, user='root', password='123456', database='day09', charset='utf8')
print(conn)
- 获取游标对象. ==========
cursor = conn.cursor()
- 执行SQL语句, 获取结果集. ==================
sql = "insert into student values(null, '刘亦菲', '女'), (null, '赵丽颖', '女');"
result = cursor.execute(sql) # 返回的是 受影响的行数
print(f"受影响的行数: {result}")
- 提交事务, 只针对于 更新语句(增删改) 有效. ===========================
conn.commit()
- 操作结果集. =========
print('添加成功!' if result > 0 else '添加失败!')
- 释放资源. ========
cursor.close()
conn.close()
PyMysql 删
def fun02():
- 获取连接对象. 主机地址 端口号 账号 密码 要连接到的数据库名 码表 ======================================
conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3306, user='root', password='123456', database='day09',charset='utf8')
- 获取游标对象. ==========
cursor = conn.cursor()
- 执行SQL语句, 获取结果集. ==================
sql = "delete from student where id=4;"
result = cursor.execute(sql) # 返回的是 受影响的行数
- 提交事务, 只针对于 更新语句(增删改) 有效. ===========================
conn.commit()
- 操作结果集. =========
print('删除成功!' if result > 0 else '删除失败!')
- 释放资源. ========
cursor.close()
conn.close()
PyMysql 改
def fun03():
- 获取连接对象. 主机地址 端口号 账号 密码 要连接到的数据库名 码表 ======================================
conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3306, user='root', password='123456', database='day09', charset='utf8')
- 获取游标对象. ==========
cursor = conn.cursor()
- 执行SQL语句, 获取结果集. ==================
sql = "update student set name='乔峰' where id = 1;"
result = cursor.execute(sql) # 返回的是 受影响的行数, 如果未修改数据, 则返回: 0
- 提交事务, 只针对于 更新语句(增删改) 有效. ===========================
conn.commit()
- 操作结果集. =========
print('修改成功!' if result > 0 else '修改失败!')
- 释放资源. ========
cursor.close()
conn.close()
PyMysql 查
def fun04():
- 获取连接对象. 主机地址 端口号 账号 密码 要连接到的数据库名 码表 ======================================
conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3306, user='root', password='123456', database='day09', charset='utf8')
- 获取游标对象. ==========
cursor = conn.cursor()
- 执行SQL语句, 获取结果集. ==================
sql = "select id, name from student where id <= 5;"
cursor.execute(sql)
results = cursor.fetchall() # 获取结果集中所有的数据.
- 提交事务, 只针对于 更新语句(增删改) 有效. 针对于查询语句 无效. =======================================
这里无需提交事务.
- 操作结果集. =========
print(f'结果集: {results}') # 格式: ((第1行数据), (第2行数据), ...)
- 释放资源. ========
cursor.close()
conn.close()
在main方法中测试.
if name == 'main':
调用 fun01() 函数, 实现: PyMysql 增 的功能演示.
fun01()
调用 fun02() 函数, 实现: PyMysql 删 的功能演示.
fun02()
调用 fun03() 函数, 实现: PyMysql 改 的功能演示.
fun03()
调用 fun04() 函数, 实现: PyMysql 查 的功能演示.
fun04()
```
7.扩展_PyMysql抽取公共函数
> 严格意义上将, 是在: 抽取工具类, 即: 把重复的动作定义到工具类中.
```python
自定义的模块(充当: 工具类), 里边定义的都是 PyMysql相关的最基本的操作, 用于简化刚才 PyMysql-CURD中 大量重复代码的.
因为受到目前所学知识点的限制, 很多内容例如: 面向对象, 魔法方法, 封装很多内容都没学, 所以我们仅仅是: 模拟 工具模块(工具类)的 思维.
导包.
import pymysql
- 自定义函数, 获取连接对象. =================
def get_conn(database_name):
"""
获取连接对象的
:param database_name: 要连接到的数据库名
:return: PyMysql的连接对象.
"""
conn = pymysql.connect(
host='localhost',
port=3306,
user='root',
password='123456',
database=database_name,
charset='utf8')
return conn
- 自定义函数, 获取游标对象. =================
def get_cursor(database_name):
"""
获取游标对象的
:param database_name: 要连接到的数据库名
:return: 游标对象
"""
2.1 调用自定义的 get_conn()函数, 获取连接对象.
conn = get_conn(database_name)
2.2 获取游标对象
cursor = conn.cursor()
2.3 返回游标对象.
return cursor
return cursor, conn # 同时返回游标对象, 连接对象.
3.自定义函数, 用于释放资源.
def release(cursor, conn):
"""
关闭连接 和 游标对象, 释放资源
:param cursor: 游标对象
:param conn: 连接对象
:return: 无
"""
如果对象不为空, 就关闭.
if cursor:
cursor.close()
if conn:
conn.close()
- 定义通用的函数, 用于执行 更新语句. ======================
def my_execute_update(database_name, sql):
4.0 获取连接对象.
conn = get_conn(database_name)
4.1 获取游标对象.
方式1: 通过自定义函数, 获取游标.
cursor = get_cursor(database_name)
方式2: 通过连接对象, 获取游标.
cursor = conn.cursor()
4.2 执行sql语句, 获取结果集(受影响行数).
rows = cursor.execute(sql)
4.3 提交事务.
conn.commit()
4.4 打印结果.
print('操作成功!' if rows > 0 else '操作失败!')
4.5 释放资源
release(cursor, conn)
- 定义通用的函数, 用于执行 查询语句. ======================
def my_execute_query(database_name, sql):
5.1 获取游标对象.
cursor = get_cursor(database_name)
5.2 执行sql语句.
cursor.execute(sql)
5.3 获取查询结果.
results = cursor.fetchall()
5.4 释放资源
release(cursor, None)
5.5 返回查询结果.
return results
```
8.测试-自定义的工具模块
```python
案例: 测试刚才自定义的 工具模块.
from my_utils import *
在main函数中测试.
if name == 'main':
- 测试执行 查询SQL 操作. =================
sql = "select id, name from student where id <= 5;"
results = my_execute_query('day09', sql)
==========================================
results = my_execute_query('day10', sql)
print(results)
- 测试执行 更新SQL 操作. =================
sql = "update student set name='小明' where id = 1;"
my_execute_update('day10', sql)
- 获取连接对象. ==========
conn = get_conn('day09')
print(conn)
- 获取游标对象. ==========
cursor = get_cursor('day10')
print(cursor)
```
9.今日内容涉及到的SQL语句
```sql
查看所有的数据库.
show databases ;
建库, 切库
create database day09 charset 'utf8';
create database day10 charset 'utf8';
use day09;
use day10;
查看所有的数据表
show tables;
建表, 添加表数据.
create table student(
id int primary key auto_increment, # id, 主键自增.
name varchar(20), # 学生姓名.
gender varchar(10) # 学生性别
);
添加表数据
insert into student values(null, '乔峰', '男'), (null, '虚竹', '男'), (null, '王语嫣', '女');
insert into student values(null, '张无忌', '男');
查看表数据.
select * from student;
insert into student values(null, '王二麻子', '男'), (null, '李政贤', '未知'), (null, '徐志胜', '男');
```
 51工具盒子
51工具盒子